The iPhone 13 Pro is the second model from the top in Apple’s 2021 smartphone line-up. The main difference to the top-of-the-line iPhone 13 Pro Max is the smaller 6.1-inch Super Retina XDR display (versus 6.7-inch on the Max). Both models are powered by Apple’s latest A15 Bionic chipset and come with up to 1TB of internal storage. They also share the same camera which has been improved in several areas compared to last year’s iPhone 12 Pro and Pro Max models.
The primary camera module features a larger sensor and faster aperture than on the 2020 models. It also uses sensor shift OIS, which last year was exclusive to the Pro Max device. The ultra-wide camera comes with a same-size sensor as last year but has gained a faster aperture and and a PDAF autofocus versus the fixed-focus lens on the iPhone 12 series. Sensor size remains unchanged in the tele module but Apple has increased the focal length and the tele now offers a 3x optical magnification compared to the primary cam.
Read on to find out how the iPhone 13 Pro camera performed in our DXOMARK Camera tests.
Overview
Key camera specifications:
- Primary: 12 MP sensor, 1.9µm pixels, 26 mm equivalent f/1.5-aperture lens, sensor shift OIS, Dual Pixel AF
- Ultra-wide: 12MP sensor, 13mm equivalent f/1.8-aperture lens, PDAF, 2cm macro
- Tele: 12 MP sensor, 77mm equivalent f/2.8-aperture lens, OIS
- 3D sensor
- 4K at 24/25/30/60 fps, 1080p at 25/30/60 fps, HDR video recording with Dolby Vision
- Cinematic mode for recording videos with shallow depth of field (1080p at 30 fps)
Scoring
Sub-scores and attributes included in the calculations of the global score.

Apple iPhone 13 Pro


Use cases & Conditions
Use case scores indicate the product performance in specific situations. They are not included in the overall score calculations.
Outdoor
Photos & videos shot in bright light conditions (≥1000 lux)
Indoor
Photos & videos shot in good lighting conditions (≥100lux)
Lowlight
Photos & videos shot in low lighting conditions (<100 lux)
Friends & Family
Portrait and group photo & videos
 7th
7th
 7th
7th
Pros
- Accurate and repeatable target exposure
- Nice color and white balance
- Nice skin tones in most light conditions, even in complex backlit scenes
- Fast, accurate and repeatable autofocus
- Good detail in indoor and outdoor conditions
- Accurate and stable target exposure with fairly wide dynamic range in video
- Well-managed texture/noise trade-off in video
- Accurate white balance indoors and outdoors, smooth transitions in scene changes
- Good autofocus tracking and smooth refocusing
Cons
- Luminance noise on primary, ultra-wide and tele, especially in low light
- Limited dynamic range in challenging high contrast scenes
- Artifacts including flare, slight ringing, and color quantization
- Limited detail in long-range zoom shots
- Occasional pink white balance casts in some conditions and some white balance variations in videos
- Lens flare and ghosting, especially in low light video
- Some loss of texture in video, especially on faces in daylight and indoor conditions
- Sharpness differences between video frames and strong residual motion in video that is recorded while running
Test summary
About DXOMARK Camera tests: DXOMARK’s Camera evaluations take place in laboratories and in real-world situations using a wide variety of subjects. The scores rely on objective tests for which the results are calculated directly by measurement software on our laboratory setups, and on perceptual tests in which a sophisticated set of metrics allow a panel of image experts to compare aspects of image quality that require human judgment. Testing a smartphone involves a team of engineers and technicians for about a week. Photo, Zoom, and Video quality are scored separately and then combined into an Overall score for comparison among the cameras in different devices. For more information about the DXOMARK Camera protocol, click here. More details on smartphone camera scores are available here. The following section gathers key elements of DXOMARK’s exhaustive tests and analyses. Full performance evaluations are available upon request. Please contact us on how to receive a full report.
The Apple iPhone 13 Pro mingles among the very best devices in our camera ranking. Like for all iPhones, color rendering is vivid with nice skin tones and a slightly warm touch, and the camera is generally very reliable, consistently producing high-quality images in all shooting situations. Overall Photo performance is quite similar to the 12 Pro that we tested last year, but improvements have been made in several areas.
Color and contrast have been improved on backlit portraits, and images show higher levels of detail, especially when shooting under typical indoor conditions. It looks like Apple’s camera engineers have managed using the new sensor’s bigger pixel pitch to improve detail preservation but, like on the 12 Pro, luminance noise is still visible in most shooting situations.
The camera’s Zoom score isn’t quite up there with the very best, but performance has still been improved over the 12 Pro, thanks to the longer 3x optical zoom versus 2x on the older model.
The outstanding Video score puts the iPhone 13 Pro at the very top of this sub-ranking, thanks to several improvements in key areas. Tone-mapping instabilities that were very visible on the iPhone 12 series model have been fixed and exposure is now generally very stable. Autofocus performance has been pushed as well, thanks to better tracking and very smooth refocusing at the right moments. Our testers did not spot any unwanted focus breathing either.
Overall it’s fair to say Apple has managed to get the most out of its imaging hardware as most higher-positioned devices in our ranking come with larger and higher resolution sensors in their primary cameras.
Photo
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
152
For scoring and analysis, DXOMARK engineers capture and evaluate more than 2,600 test images both in controlled lab environments and in outdoor, indoor and low-light natural scenes, using the camera’s default settings. The photo protocol is designed to take into account the main use cases and is based on typical shooting scenarios, such as portraits, family, and landscape photography. The evaluation is performed by visually inspecting images against a reference of natural scenes, and by running objective measurements on images of charts captured in the lab under different lighting conditions from 1 to 1,000+ lux and color temperatures from 2,300K to 6,500K.
In this section, we take a closer look at each sub-attribute and compare image quality against competitors. Please note that the iPhone 13 Pro camera comes with a set of photo styles and users are asked for their preferred option when launching the camera app for the first time. You can choose between pre-defined photo styles or customize your own, using Tone and Warmth sliders. These settings modify both color and exposure. We skipped this option for our tests and used default settings as usual.
The Apple iPhone 13 Pro uses its ultra-wide camera when switching to macro mode, allowing it to capture images at very short distances. The resulting magnification is close to 1:1 with a pretty interesting level of detail at the center of the frame.

Exposure
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
117
Exposure is one of the key attributes for technically good pictures. The main attribute evaluated is the brightness of the main subject through various use cases such as landscape, portrait, or still life. Other factors evaluated are the contrast and the dynamic range, eg. the ability to render visible details in both bright and dark areas of the image. Repeatability is also important because it demonstrates the camera's ability to provide the same rendering when shooting several images of the same scene.
The Apple iPhone 13 Pro produces accurate and repeatable target exposure in most tested conditions. However, dynamic range is often limited, resulting in highlight clipping in high-contrast scenes. It’s also worth mentioning that in the gallery app highlights in photos are rendered almost “aggressively” bright, which can contribute to the impression of clipping. On a standard screen the effect is less pronounced.
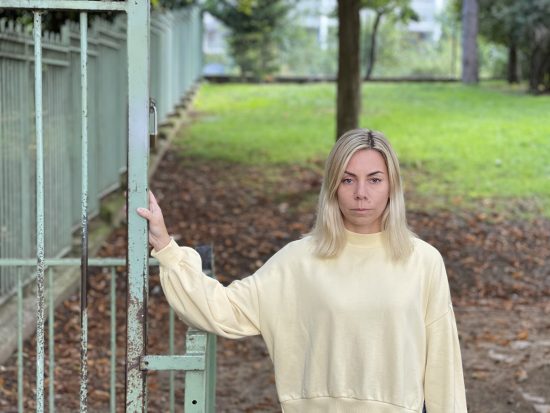
These samples show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s exposure performance in a backlit scene.

Color
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
119
Color is one of the key attributes for technically good pictures. The image quality attributes analyzed are skin-tone rendering, white balance, color shading, and repeatability. For color and skin tone rendering, we penalize unnatural colors but we respect a manufacturer's choice of color signature.
The Apple’s color rendering and white balance are generally pleasant, and the camera captures very nice skin tones. Especially in high-contrast scenes, the iPhone 13 Pro’s skin tones are better than the competition’s. It seems like the camera uses adaptive color rendering that adjusts to the captured skin tones and light conditions.
These samples show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s color performance in a backlit scene.
In night images, the iPhone 13 Pro captures good detail in faces when the flash triggers. However, dynamic range is limited, which leads to highlight clipping and underexposed backgrounds. These samples show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s night performance in flash-off mode.

Autofocus
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
116
Autofocus tests concentrate on focus accuracy, focus repeatability, shooting time delay, and depth of field. Shooting delay is the difference between the time the user presses the capture button and the time the image is actually taken. It includes focusing speed and the capability of the device to capture images at the right time, what is called 'zero shutter lag' capability. Even if a shallow depth of field can be pleasant for a single subject portrait or close-up shot, it can also be a problem in some specific conditions such as group portraits; Both situations are tested. Focus accuracy is also evaluated in all the real-life images taken, from infinity to close-up objects and in low light to outdoor conditions.
The Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s autofocus is fast, accurate and repeatable in most conditions. Depth of field is slightly limited which is due to the larger sensor compared to the iPhone 12 series. Unlike Xiaomi on the Mi 11 Ultra Apple does not apply any image processing to increase sharpness of background subjects.
This graph shows the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s autofocus performance in the lab at a light level of 100 lux. Autofocus is fast and accurate with negative shutter lag, even in high dynamic range conditions (EV 7).
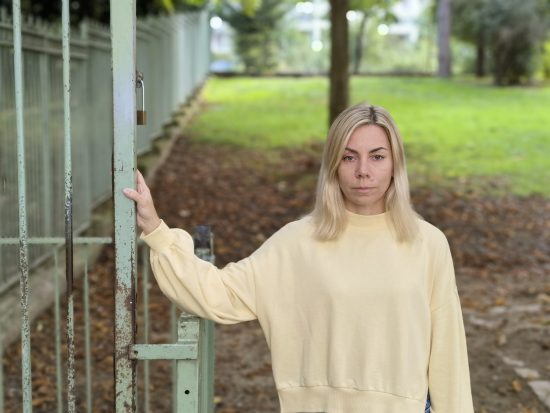
These samples show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s depth of field.

Texture
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
114
Texture tests analyze the level of details and the texture of subjects in the images taken in the lab as well as in real-life scenarios. For natural shots, particular attention is paid to the level of details in the bright and dark areas of the image. Objective measurements are performed on chart images taken in various lighting conditions from 1 to 1000 lux and different kinds of dynamic range conditions. The charts used are the proprietary DXOMARK chart (DMC) and the Dead Leaves chart.
Details in the iPhone 13 Pro are slightly higher than on its predecessor the iPhone 12 Pro but still slightly below the best in class, such as the Xiaomi Mi 11 Ultra. These samples show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s texture performance in daylight conditions.
This graph shows the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s texture performance in the lab across varying light levels

Noise
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
115
Noise tests analyze various attributes of noise such as intensity, chromaticity, grain, structure on real-life images as well as images of charts taken in the lab. For natural images, particular attention is paid to the noise on faces, landscapes, but also on dark areas and high dynamic range conditions. Noise on moving objects is also evaluated on natural images. Objective measurements are performed on images of charts taken in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux and different kinds of dynamic range conditions. The chart used is the Dead Leaves chart and the standardized measurement such as Visual Noise derived from ISO 15739.
Luminance noise is visible in most conditions, especially in low light, and stronger than on some competitors. However, we’re mostly dealing with very fine grained luminance noise here, which is much less intrusive than bigger noise “blobs” and can even result in an impression of better detail.
This graph shows the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s noise performance in the lab across light levels.
These samples show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s noise performance in indoor conditions.

Artifacts
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
81
The artifacts evaluation looks at lens shading, chromatic aberrations, geometrical distortion, edges ringing, halos, ghosting, quantization, unexpected color hue shifts, among others type of possible unnatural effects on photos. The more severe and the more frequent the artifact, the higher the point deduction on the score. The main artifacts observed and corresponding point loss are listed below.
Image flare is frequently visible in all conditions. The same is true for ringing, aliasing, ghosting, and color quantization. However, compared to the iPhone 12 Pro Max the latter has been reduced.
Bokeh
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
80
Bokeh is tested in one dedicated mode, usually portrait or aperture mode, and analyzed by visually inspecting all the images captured in the lab and in natural conditions. The goal is to reproduce portrait photography comparable to one taken with a DLSR and a wide aperture. The main image quality attributes paid attention to are depth estimation, artifacts, blur gradient, and the shape of the bokeh blur spotlights. Portrait image quality attributes (exposure, color, texture) are also taken into account.
The iPhone 13 Pro camera produces a nice bokeh effect, but slight depth estimation artifacts can be noticeable. Given that the blur effect is quite strong, even small errors are quite visible. Color rendering is more pleasant than on the iPhone 12 Pro Max. These samples show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s bokeh simulation in daylight.
Preview
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
91
Preview tests analyze the image quality of the camera app's preview of the image, with particular attention paid to the difference between the capture and the preview, especially regarding dynamic range and the application of the bokeh effect. Also evaluated is the smoothness of the exposure, color and focus adaptation when zooming from the minimal to the maximal zoom factor available. The preview frame rate is measured using the LED Universal Timer.
As with previous iPhones, the preview rendering is mostly very close to the final captured image. In this example, the iPhone 13 Pro preserves highlight detail noticeably better than the Huawei P50 Pro.
Zoom
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
151
DXOMARK engineers capture and evaluate over 400 test images in controlled lab environments and in outdoor, indoor, and low-light natural scenes, using the camera’s default settings and pinch zoom at various zoom factors from ultra wide to very long-range zoom. The evaluation is performed by visually inspecting the images against a reference of natural scenes, and by running objective measurements of chart mages captured in the lab under different conditions from 20 to 1000 lux and color temperatures from 2300K to 6500K.

Wide
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
117
These tests analyze the performance of the ultra-wide camera at several focal lengths from 12 mm to 20 mm. All image quality attributes are evaluated, with particular attention paid to such artifacts as chromatic aberrations, lens softness, and distortion. Pictures below are an extract of tested scenes.
This sample shows the performance of the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s ultra-wide camera in outdoor conditions.

Tele
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
116
All image quality attributes are evaluated at focal lengths from approximately 40 mm to 300 mm, with particular attention paid to texture and detail. The score is derived from a number of objective measurements in the lab and perceptual analysis of real-life images.
Compared with its predecessor, the iPhone 13 Pro’s tele zoom has been improved at medium range settings, but with its relatively short optical tele still shows limitations at long range. Like for the ultra-wide, it’s worth mentioning that night mode is now available on the tele lens but this is not currently tested under our protocol.
These samples show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s performance at a long-range tele setting.
Video
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
149
DXOMARK engineers capture and evaluate more than 2.5 hours of video in controlled lab environments and in natural low-light, indoor and outdoor scenes, using the camera’s default settings. The evaluation consists of visually inspecting natural videos taken in various conditions and running objective measurements on videos of charts recorded in the lab under different conditions from 1 to 1000+ lux and color temperatures from 2,300K to 6,500K.
NOTE: The sample video clips in this section are best viewed at 4K resolution.
Exposure tests evaluate the brightness of the main subject and the dynamic range, eg. the ability to render visible details in both bright and dark areas of the image. Stability and temporal adaption of the exposure are also analyzed.

Color
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
117
Image-quality color analysis looks at color rendering, skin-tone rendering, white balance, color shading, stability of the white balance and its adaption when light is changing.
White balance is accurate in bright light and under indoor conditions, with smooth adaptations when the scene changes. In low light pink casts and slight instabilities can be noticeable. These sample clips show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s video color in an outdoor scene.

Autofocus
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
117
The iPhone 13 Pro’s video autofocus has good tracking capabilities refocuses smoothly when the scene is changing. This can also be seen in Apple’s new Cinematic Mode, which automatically switches focus between foreground and background subjects, based on scene content. This new mode is not covered by our current test protocol, though.
These sample clips show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s video autofocus performance in daylight.

Texture
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
115
Texture tests analyze the level of details and texture of the real-life videos as well as the videos of charts recorded in the lab. Natural videos recordings are visually evaluated, with particular attention paid to the level of details in the bright and areas as well as in the dark. Objective measurements are performed of images of charts taken in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux. The charts used are the DXOMARK chart (DMC) and Dead Leaves chart.
The iPhone 13 Pro manages the texture/noise trade-off well in video, but texture rendering artifacts can be visible, especially on faces when recording in bright light or indoors. These sample clips show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s texture performance in low light.
This graph shows the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s detail preservation in video under different light conditions. These sample clips show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s noise performance in low light.

Noise
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
118
Noise tests analyze various attributes of noise such as intensity, chromaticity, grain, structure, temporal aspects on real-life video recording as well as videos of charts taken in the lab. Natural videos are visually evaluated, with particular attention paid to the noise in the dark areas and high dynamic range conditions. Objective measurements are performed on the videos of charts recorded in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux. The chart used is the DXOMARK visual noise chart.
This graph shows the Apple iPhone 13 Pro noise performance in the lab.

Artifacts
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
86
Artifacts are evaluated with MTF and ringing measurements on the SFR chart in the lab as well as frame-rate measurements using the LED Universal Timer. Natural videos are visually evaluated by paying particular attention to artifacts such as aliasing, quantization, blocking, and hue shift, among others. The more severe and the more frequent the artifact, the higher the point deduction from the score. The main artifacts and corresponding point loss are listed below.
This video shows a flare effect in low light.

Stabilization
Apple iPhone 13 Pro
117
Stabilization evaluation tests the ability of the device to stabilize footage thanks to software or hardware technologies such as OIS, EIS, or any others means. The evaluation looks at residual motion, smoothness, jellow artifacts and residual motion blur on walk and run use cases in various lighting conditions. The video below is an extract from one of the tested scenes.
Sharpness difference between frames is sometimes visible and strong residual motion is visible in running motion. These sample clips show the Apple iPhone 13 Pro’s stabilization performance in daylight.

 English
English 中文
中文
































DXOMARK invites our readership (you) to post comments on the articles on this website. Read more about our Comment Policy.